What is Edge Computing
Edge computing in a nutshell is moving computation, network, storage resources closer to end users/devices. Edge computing is not a new concept, it was first mentioned around more than 2 decades ago. It was the time when Akamai introduced a new idea to shift nodes geographically closer to end users to better deliver content such as images and videos. That idea is what we are familiar with today: CDN (content delivery network). CDN is the very first implementation of edge computing concept. What it has been done and continues doing is the giving a possibility to securely, seamlessly access content as fast as possible with minimum delay of network by off-loading resources to locations close to end users. Geographically off-loading resources is the key characteristic of edge computing which is implemented in multiple ways due to multiple use cases’s requirements.
(Source: https://www.ibm.com/cloud/smartpapers/5g-edge-computing/)
Why Edge Computing
Recently, edge computing has been researched, mentioned in many technical reports, blogs and there have been a lots of projects/products established in edge computing domain, however, the main reason that causes the explosion of edge computing is IoT. In the era of connected world, everything is smart and data is everything. When data is massively generated, they should be stored, analyzed, processed and utilized in a productive way. The decisive information after consuming data must be seamlessly transfered back to end user to execute prompt actions. In order to do that, a new paradigm of computing resources should be located out of traditional data centers, cloud computing
When cloud computing commercially appeared the first time in 2006, it did resolved the problem of flexible, scalable, high-volume resources providing to end-users, but it is not the solution of every use cases. In the use cases where instantaneous decision-making, for instance IoT or self-driving car is critical, the speed of processing and delivering information is crucial. Those actions should be done locally which cloud computing can not help.n
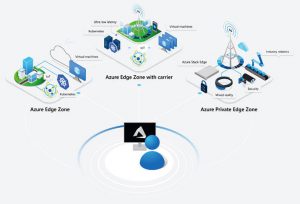
Then there appeared some new definitions such as Fog computing, Cloudlet, they are just different implementations of Edge computing. Imagine that Edge computing is what people want, it is the target so Fog computing or others are only the medium to reach that target due to use cases. In order to make the comparison between implementations, Edge Computing can be classified into multiple characteristics so it is obvious to see the differences between them. Those characteristics include Access Medium (Wifi, LTE, bluetooth, MQTT, etc.), Location, Device, Server Density, Power consumption, etc. (Source: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/319284011_Comparison_of_edge_computing_implementations_Fog_computing_cloudlet_and_mobile_edge_computing). The critical impression of each characteristic varies based on features’s requirements of different use cases, for instance, bandwidth is highly critical in AR/VR or Video caching/Analytics but not in E-Health.
What makes Edge Computing different to Cloud Computing?
– Apparently, Edge computing is the extension of Cloud Computing to end-users.
– When people talking about Cloud Computing, it is emphasized on a concept of gathering huge, scalable resources but with Edge computing, it is about Data, spontaneous decision making and some trending technologies utilizing data, for instance, AI/ML.
– In the viewpoint of data plane, Cloud Computing will be a solution to store multiple types of data, execute data engineering actions, biodata in general. However, Edge Computing is where to transfer data up to cloud as well as make near/realtime decisions based on input data from end-user/device
Emerging technologies in implementing Edge computing
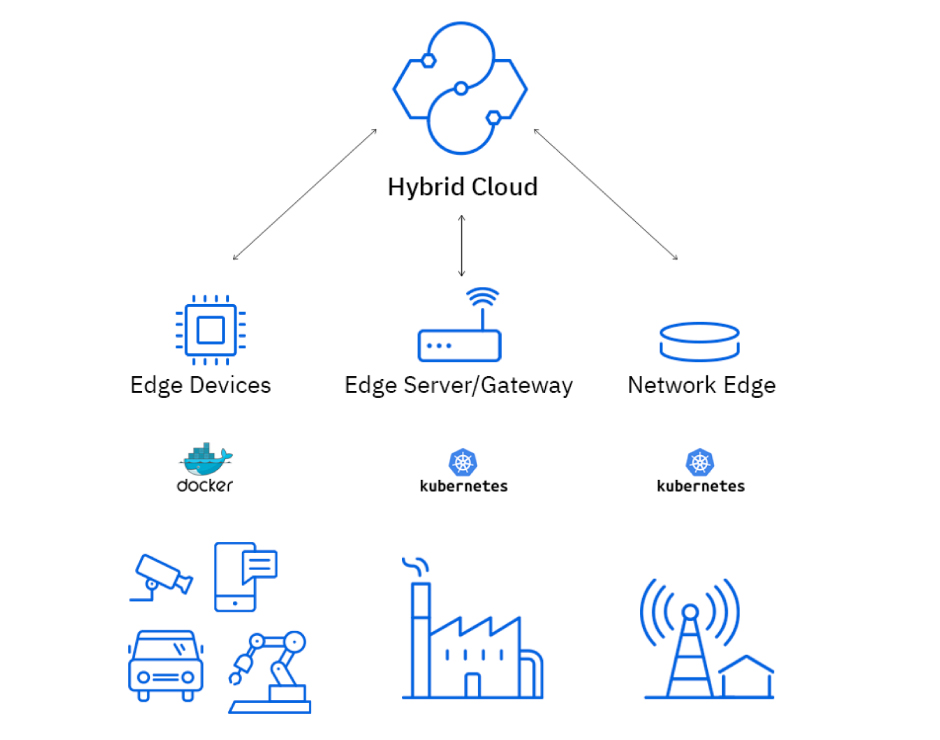
There are two main technologies applying in Edge computing: container technology and AI/ML.
In fact, container technology is chosen to be foundation of edge computing. There are some below critical criteria to justify the container technology advantages in order to fulfill the edge computing requirements:
– One of the critical feature of an Edge location is self-managed capability. Since edge location can be places where there is a limitation of network connectivity or constraints of resources (limited cpus, rams, etc.) therefore it is not easy to manage them from outside. Applications running on edge location should be able to be fault-tolerance, self-healing, running in autonomy.
– The more further to cloud data center, the more lighter size of edge device is. It needs to run an edge control plane which is enough small footprint to not consume a lot of resources.
On the other hands, as Edge computing focuses on data activities regarding to edge user/device, AI/ML is indispensable. Data from edge will be transferred to cloud to execute data engineering, data analytics, etc. to train model sand edge will be the location to deploy these trained models.
What Players should do in Edge Computing
In the past 3-5 years, edge computing and its ecosystem have become more and more popular with many projects and use cases. Besides, there are a lot of companies/organizations offering a lot of strategic plans on how to dominate the market for edge computing related services, but it is actually quite confusing since there are so many projects born neither really being used nor showing the benefits of them, etc. Ultimately, for business, the most important things must be profit. Let’s have a walkthrough.
Going through the market of edge computing projects, products, we have a series of prominent names like Akraino, EdgeX Foundry, ETSI MEC, OpenFog Consortium, Rafay Systems, Packet, Telstra, etc. Those name varies in multiple vertical markets, from micro use cases like IoT to bigger landscape of Industrial Revolution 4 (IR4). The information of the projects can be easily found on Internet but personally with a bunch of projects laying out like this, what the people ultimately want to do, what to do to take over the market, specifically visualize it? It can be seen from 3 viewpoints as well as 3 directions as follows:
– Deploy/manage/own edge locations.
– Connects/inter-manages edge nodes/locations.
– Enable edge-based applications.
To be continued ….